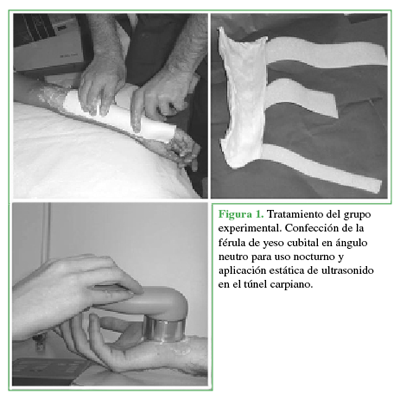
Efficacy of night splinting and ultrasound in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. A randomized controlled clinical trial
Main Article Content
Abstract
Key words: Key words: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome; therapeutics; splints; ultrasound therapy.Level of Evidence: II
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
2. Burke FD, Ellis J, McKenna H, Bradley MJ. Primary care management of carpal tunnel syndrome. Postgrad Med J
2003;79(934):433-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/pmj.79.934.433
3. Jablecki CK, Andary MT, Floeter MK, Miller RG, Quartly CA, Vennix MJ, et al. Practice parameter:
Electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Report of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic
Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
Neurology 2002;58(11):1589-92. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.58.11.1589
4. Currier DP, Greathouse D, Swift T. Sensory nerve conduction: effect of ultrasound. Arch Phys Med Rehabil
1978;59(4):181-5. PMID: 646607
5. Kramer JF. Effect of therapeutic ultrasound intensity on subcutaneous tissue temperature and ulnar nerve conduction velocity. Am J Phys Med 1985;64(1):1-9. PMID: 3970155
6. Ebenbichler GR, Resch KL, Nicolakis P, Wiesinger GF, Uhl F, Ghanem AH, et al. Ultrasound treatment for treating the carpal tunnel syndrome: randomised “sham” controlled trial. BMJ 1998;316(7133):731-5.
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.316.7133.731
7. Page MJ, O’Connor D, Pitt V, Massy-Westropp N. Therapeutic ultrasound for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev 2013;2013( 3):CD009601. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009601.pub2
8. Werner CO, Elmqvist D, Ohlin P. Pressure and nerve lesion in the carpal tunnel. Acta Orthop Scand
1983;54(2):312-6. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453678308996576
9. Kruger VL, Kraft GH, Deitz JC, Ameis A, Polissar L. Carpal tunnel syndrome: objective measures and splint use.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1991;72(7):517-20. PMID: 2059127
10. Page MJ, Massy-Westropp N, O’Connor D, Pitt V. Splinting for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;2012(7):CD010003. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010003
11. Halac G, Demir S, Yucel H, Niftaliyev E, Kocaman G, Duruyen H, et al. Splinting is effective for night-only
symptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome patients. J Phys Ther Sci 2015;27(4):993-6. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.993
12. Armenteros Pedrero J, Justo García G, Rey Pita ML, Gallego González S, Buján de Gonzalo A, Tobío Iglesias
A. Tratamiento conservador del síndrome del túnel carpiano mediante inmovilización con férulas. Rehabilitación
(Madr) 2000; 34(4): 313-9. https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-rehabilitacion-120-articulo-tratamiento-conservador-del-sindrome-del-10017830
13. Massy-Westropp N, Grimmer K, Bain G. A systematic review of the clinical diagnostic tests for carpal tunnel
syndrome. J Hand Surg Am 2000;25(1):120-7. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhsu.2000.jhsu025a0120
14. Gallagher EJ, Liebman M, Bijur PE. Prospective validation of clinically important changes in pain severity
measured on a visual analog scale. Ann Emerg Med 2001;38(6):633-8. https://doi.org/10.1067/mem.2001.118863
15. Stratford P, Gill C, Westaway M, Binkley J. Assessing disability and change on individual patients: a report of a
patient specific measure. Physiother Can 1995;47(4):258-63. https://doi.org/10.3138/ptc.47.4.258
16. Hefford C, Abbott JH, Arnold R, Baxter GD. The patient-specific functional scale: validity, reliability, and
responsiveness in patients with upper extremity musculoskeletal problems. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2012;42(2):56-65. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2012.3953
17. Ng CL, Ho DD, Chow SP. The Moberg pickup test: results of testing with a standard protocol. J Hand Ther
1999;12(4):309-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0894-1130(99)80069-6
18. Stamm TA, Ploner A, Machold KP, Smolen J. Moberg picking-up test in patients with inflammatory joint
diseases: a survey of suitability in comparison with button test and measures of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum
2003;49(5):626-32. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11378
19. Baysal O, Altay Z, Ozcan C, Ertem K, Yologlu S, Kayhan A. Comparison of three conservative treatment protocols in carpal tunnel syndrome. Int J Clin Pract 2006;60(7):820-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.00867.x
20. Armagan O, Bakilan F, Ozgen M, Mehmetoglu O, Oner S. Effects of placebo-controlled continuous and pulsed
ultrasound treatments on carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized trial. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2014;69(8):524-8.
https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2014(08)04
21. Dincer U, Cakar E, Kiralp MZ, Kilac H, Dursun H. The effectiveness of conservative treatments of carpal tunnel
syndrome: splinting, ultrasound, and low-level laser therapies. Photomed Laser Surg 2009;27(1):119-25.
https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2008.2211
22. Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C, Ortega-Santiago R, Díaz HF, Salom-Moreno J, Cleland JA, Pareja JA, et al. Costeffectiveness evaluation of manual physical therapy versus surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome: evidence from a randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2019;49(2):55-63. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2019.8483
23. Huisstede BM, Hoogvliet P, Randsdorp MS, Glerum S, van Middelkoop M, Koes BW. Carpal tunnel syndrome.
Part I: effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments—a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2010;91(7):981-1004.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2010.03.022
24. Huisstede BM, Hoogvliet P, Franke TP, Randsdorp MS, Koes BW. Carpal tunnel syndrome: effectiveness of
physical therapy and electrophysical modalities. An updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2018;99(8):1623-34.e23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2017.08.482
25. Bakhtiary AH, Rashidy-Pour A. Ultrasound and laser therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Aust J Physiother 2004;50(3):147-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0004-9514(14)60152-5