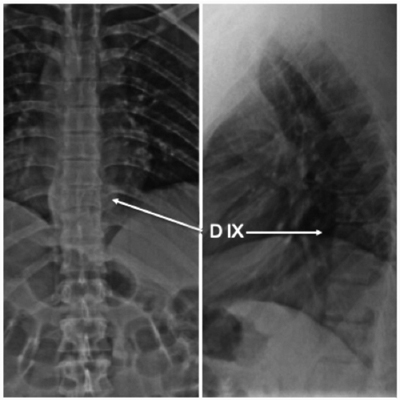
Acute Paraparesis due to Aggressive Vertebral Hemangioma. Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Main Article Content
Abstract
Conclusion: Through early decompression and arthrodesis followed by local adjuvant radiotherapy, we obtained complete neurological recovery and disease control in a medium-term follow-up.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
hemangiomas. J Neurosurg 1993;(7881):36-45. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.78.1.0036
2. Huvos AG. Hemangioma, lymphangioma, angiomatosis/lymphangiomatosis, glomus tumor. En: Huvos AG (ed.). Bone tumors: diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1991:553-78.
3. Rudnick J, Stern M. Symptomatic thoracic vertebral hemangioma: a case report and literature review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85(9):1544-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2003.08.099
4. Cross JJ, Antoun NM, Laing RJ, Xuereb J. Imaging of compressive vertebral haemangiomas. Eur Radiol
2000;10(6):997-1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300051051
5. Gaudino S, Martucci M, Colantonio R, Lozupone E, Visconti E, Leone A, et al. A systematic approach to vertebral
hemangioma. Skeletal Radiol 2015;44(1):25-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2035-y
6. Orrison W. Neuroimaging. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co; 2000:1335-6.
7. Osborn A. Diagnostic neuroradiology. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1994:877-9.
8. Enneking WF. Musculoskeletal tumor staging: 1988 update. Cancer Treat Res 1989;44:39-49.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-1757-9_3
9. Healy M, Rerz DA, Pearl L. Spinal hemangiomas. Neurosurgery 1985;13(6):689-91.
https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198312000-00013
10. Templin CR, Stambough JB, Stambough JL. Acute spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangiomas.
Spine J 2004;4(5):595-600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2003.08.034
11. Castel E, Lazennec JY, Chiras J, Enkaoua E, Saillant G. Acute spinal cord compression due to intraspinal bleeding from a vertebral hemangioma: two case-reports. Eur Spine J 1999;8(3):244-8.
https://doi.org/:10.1007/s005860050167
12. Ahn H, Jhaveri S, Yee A, Finkelstein J. Lumbar vertebral hemangioma causing cauda equina syndrome: a case
report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30(21):662-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000184560.78192.f6
13. Nguyen JP, Djinjian M, Pavlovitch JM, Badiane S. Vertebral hemangioma with neurologic signs: therapeutic results. Neurochirurgie 1989;35(5):299-303, 305-8. PMID: 2630927
14. Campanacci M. Hemangioma. En: Campanacci M (ed.). Bone and soft tissue tumors. Padova: Piccin Nuova Libraria &Wien: Springer; 1999:599-618.
15. Nurick S. The pathogenesis of the spinal cord disorder associated with cervical spondylosis. Brain 1972;95(1):87-100. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/95.1.87
16. Tetreault L, Kopjar B, Nouri A, Arnold P, Barbagallo G, Bartels R, et al. The modified Japanese Orthopaedic
Association scale: establishing criteria for mild, moderate and severe impairment in patients with degenerative
cervical myelopathy. Eur Spine J 2017;26(1):78-84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4660-8
17. Persaud T. The polka-dot sign. Radiology 2008;246(3):980-1. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2463050903
18. Wang B, Zhang L, Yang S, Han S, Jiang L, Wei F, et al. Atypical radiographic features of aggressive vertebral
hemangiomas. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2019;101(11):979-86. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.18.00746
19. Acosta FL, Sanai N, Cloyd J, Deviren V, Chou D, Ames CP. Treatment of Enneking stage 3 aggressive vertebral
hemangiomas with intralesional spondylectomy: report of 10 cases and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech 2011;24(4):268-75. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181efe0a4
20. Qiu B, Joo P, Ajabnoor R, Boyce B, Mesfin A. Surgical management of aggressive hemangiomas of the spine. J Clin Neurosci 2020;78:67-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2020.06.012
21. Heiss JD, Doppman JL, Olfield EH. Brief report: relief of spinal cord compression from vertebral hemangioma by intralesional injection of absolute etanol. N Engl J Med 1994;331(8):508-11. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199408253310804
22. Hekster REM, Luyendijk W, Tan TI. Spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangiomas relieved by
percutaneous catheter embolisation. Neuroradiology 1972;3:160-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341502
23. Hao J, Hu Z. Percutaneous cement vertebroplasty in the treatment of symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas. Pain Physician 2012;15(1):43-9. PMID: 22270737
24. Pinto M, Añon M, D’Innocenzo AC, Gomez AA, Zanabria Sosa C, Gonzalez FJ. Cifoplastia con balón para el
tratamiento de los hemangiomas vertebrales. Descripción de un caso y revisión bibliográfica. Rev Asoc Arg Ortop
Traumatol 2009;74(1):66-9. Disponible en: https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/2009/n1/art11.pdf
25. Garzon-Muvdi T, Iyer R, Goodwin CR, Abu-Bonsrah N, Orru E, Gailloud P, et al. Percutaneous embolization and
spondylectomy of an aggressive L2 hemangioma. Spine J 2016;16(3):167-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2015.10.001
26. Jaramillo Carling E. Compresión medular causada por hemangioma vertebral. Presentación de un caso y análisis de la literatura médica. Rev Colomb Ortop Traumatol 2005;19(1):86-9. Disponible en: http://www.sccot.org.co/pdf/RevistaDigital/19-01-2005/14Compresion.pdf
27. Sewell MD, Dbeis R, Bliss P, Watkinson T, Hutton M. Radiotherapy for acute, high-grade spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangioma. Spine J 2016;16(3):195-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2015.10.018
28. Rades D, Bajrovic A, Alberti W, Rudat V. Is there a dose-effect relationship for the treatment of symptomatic
vertebral hemangioma? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;55(1):178-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03734-3
29. Kaoudi A, Capel C, Chenin L, Peltier J, Lefranc M. Robot-assisted radiofrequency ablation of a sacral s1–s2
aggressive hemangioma. World Neurosurg 2018;116:226-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.060
30. Manning HJ. Symptomatic hemangioma of the spine. Radiology 1951;56(1):58-65. https://doi.org/10.1148/56.1.58
31. Raco A, Ciappetta P, Artico M, Salvati M, Guidetti G, Guglielmi G. Vertebral hemangiomas with cord compression: the role of embolization in five cases. Surg Neurol 1990;34(3):164-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(90)90067-y
32. Grau SJ, Holtmannspoetter M, Seelos K, Tonn JC, Siefert A. Giant multilevel thoracic hemangioma with spinal
cord compression in a patient with Klippel-Weber-Trenaunay syndrome: case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976)
2009;34(14):E498-E500. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a4e4b8
33. Wang GX, Mu YD, Che JY, Zhang GF, Jiang G, Gao CP. Compressive myelopathy and compression fracture of
aggressive vertebral hemangioma after parturition: A case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore)
2019;98(50):e18285. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018285