The LRINEC score diagnostic value for necrotizing infections of the upper extremity and correlation with morbidity and mortality in Orthopedics patients
Main Article Content
Abstract
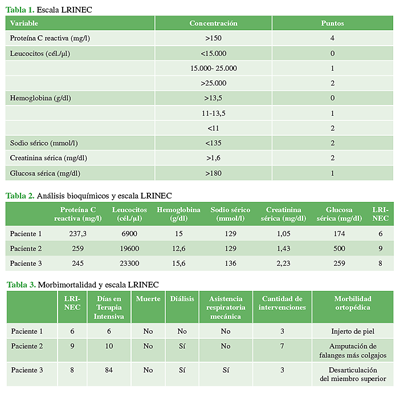
Materials and Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the medical records of patients operated on by our team between March 1, 2015, and March 1, 2020. Data collection included the LRINEC scores of every patient who underwent surgery and had a clinical and postoperative diagnosis of necrotizing soft tissue infection, as well as their clinical history, causative organism, complications, Orthopedics-related morbidity and mortality data, and other significant clinical data (length of intensive care stay, need for mechanical respiratory assistance, need for dialysis, number of surgeries), which were then compared with their respective LRINEC score.
Results: The review included 4126 medical records of patients who had undergone surgery by our team. There were three recorded cases of necrotizing infections in the upper extremity. Their LRINEC scores were retrospectively calculated and all of them showed a high risk of developing a necrotizing infection. The patients with the highest scores developed more Orthopedics and other clinical conditions.
Conclusions: The LRINEC score is a reproducible method for the diagnosis of necrotizing soft tissue infections and is related to the number of complications and orthopedic conditions, although not necessarily with the number of surgeries.
Key words: Necrotizing infection; LRINEC score; morbidity; necrotizing fasciitis.Level of Evidence: II
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
2. Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Bassetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis, and
management. J Trauma 2012;72(3):560-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318232a6b3
3. Tunovic E, Gawazuik J, Bzura T, Embil J, Esmail A, Logsetty S. Necrotizing fasciitis: A six-year experience. J Burn
Care Res 2012;33(1):93-100. https://doi.org/10.1097/BCR.0b013e318239d571
4. Lee A, May A, Obremskey WT. Necrotizing soft-tissue infections: an orthopaedic emergency. J Am Acad Orthop
Surg 2019;27(5): e199-e206. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00616
5. Magala J, Makobore P, Makumbi T, Kaggwa S, Kalanzi E, Galukande M. The clinical presentation and early
outcomes of necrotizing fasciitis in a Ugandan Tertiary Hospital–a prospective study. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:476.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-476
6. Misiakos EP, Bagias G, Patapis P, Sotiropoulos D, Kanavidis P, Machairas A. Current concepts in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Front Surg 2014;1:36. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2014.00036
7. Shiroff AM, Herlitz GN, Gracias VH. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. J Intensive Care Med 2014;29(3):138-44.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066612463680
8. Wong C-H, Khin L-W, Heng K-S, Tan K-C, Low C-O. The LRINEC (laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing
fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotising fasciitis from other soft-tissue infections. Crit Care Med 2004;
32(7):1535-41. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000129486.35458.7d
9. Wilson MP, Schneir AB. A case of necrotizing fasciitis with a LRINEC score of zero: clinical suspicion should
trump scoring systems. J Emerg Med 2013;44(5):928-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2012.09.039
10. Holland MJ. Application of the laboratory risk indicator in necrotising fasciitis (LRINEC) score to patients in a
tropical tertiary referral centre. Anaesth Intensive Care 2009; 37(4): 588-92. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X0903700416
11. Hakkarainen TW, Kopari NM, Pham TN, Evans HL. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: review and current concepts in treatment, systems of care, and outcomes. Curr Probl Surg 2014; 51: 344-62. https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpsurg.2014.06.001
12. Tsai Y-H, Hsu RW-W, Huang K-C, Huang T-J. Laboratory indicators for early detection and surgical treatment of vibrio necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468(8):2230-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1311-y
12. Chao W-N, Tsai S-J, Tsai C-F, Su C-H, Chan K-S, Lee Y-T, et al. The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing
Fasciitis score for discernment of necrotizing fasciitis originated from Vibrio vulnificus infections. J Trauma Acute
Care Surg 2012;73(6): 1576-82. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318270d761
14. Liao C-I, Lee Y-K, Su Y-C, Chuang C-H, Wong C-H. Validation of the laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing
fasciitis (LRINEC) scorefor early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Tzu Chi Medical J 2012;24(2):73-6. https://doi.
org/10.1016/j.tcmj.2012.02.009
15. Borschitz T, Schlicht S, Siegel E, Hanke E, von Stebut E. Improvement of a clinical score for necrotizing fasciitis:
‘Pain out of proportion’ and high CRP levels aid the diagnosis. PLoS One 2015;10(7):e0132775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132775
16. Bechar J, Sepehripour S, Hardwicke J, Filobbos G. Laboratory risk indicator for necrotising fasciitis (LRINEC)
score for the assessment of early necrotising fasciitis: a systematic review of the literature. Ann R Coll Surg Engl
2017;99(5):341-6. https://doi.org/10.1308/rcsann.2017.0053