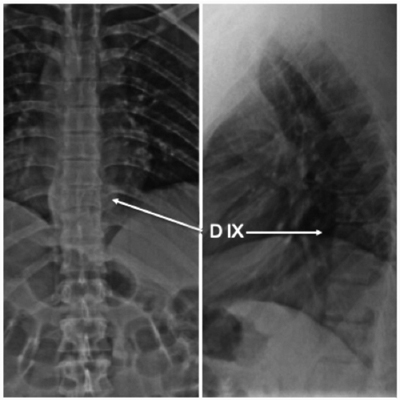
Paraparesia aguda por hemangioma vertebral agresivo. Reporte de dos casos y revisión bibliográfica
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Conclusión: Mediante la descompresión y la artrodesis tempranas seguidas de radioterapia, se logró la recuperación neurológica completa y el control de la enfermedad en un seguimiento a mediano plazo.
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo
La aceptación del manuscrito por parte de la revista implica la no presentación simultánea a otras revistas u órganos editoriales. La RAAOT se encuentra bajo la licencia Creative Commons 4.0. Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Se puede compartir, copiar, distribuir, alterar, transformar, generar una obra derivada, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente la obra, siempre que: a) se cite la autoría y la fuente original de su publicación (revista, editorial y URL de la obra); b) no se usen para fines comerciales; c) se mantengan los mismos términos de la licencia.
En caso de que el manuscrito sea aprobado para su próxima publicación, los autores conservan los derechos de autor y cederán a la revista los derechos de la publicación, edición, reproducción, distribución, exhibición y comunicación a nivel nacional e internacional en las diferentes bases de datos, repositorios y portales.
Se deja constancia que el referido artículo es inédito y que no está en espera de impresión en alguna otra publicación nacional o extranjera.
Por la presente, acepta/n las modificaciones que sean necesarias, sugeridas en la revisión por los pares (referato), para adaptar el trabajo al estilo y modalidad de publicación de la Revista.
Citas
hemangiomas. J Neurosurg 1993;(7881):36-45. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.78.1.0036
2. Huvos AG. Hemangioma, lymphangioma, angiomatosis/lymphangiomatosis, glomus tumor. En: Huvos AG (ed.). Bone tumors: diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1991:553-78.
3. Rudnick J, Stern M. Symptomatic thoracic vertebral hemangioma: a case report and literature review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85(9):1544-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2003.08.099
4. Cross JJ, Antoun NM, Laing RJ, Xuereb J. Imaging of compressive vertebral haemangiomas. Eur Radiol
2000;10(6):997-1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300051051
5. Gaudino S, Martucci M, Colantonio R, Lozupone E, Visconti E, Leone A, et al. A systematic approach to vertebral
hemangioma. Skeletal Radiol 2015;44(1):25-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2035-y
6. Orrison W. Neuroimaging. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co; 2000:1335-6.
7. Osborn A. Diagnostic neuroradiology. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1994:877-9.
8. Enneking WF. Musculoskeletal tumor staging: 1988 update. Cancer Treat Res 1989;44:39-49.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-1757-9_3
9. Healy M, Rerz DA, Pearl L. Spinal hemangiomas. Neurosurgery 1985;13(6):689-91.
https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198312000-00013
10. Templin CR, Stambough JB, Stambough JL. Acute spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangiomas.
Spine J 2004;4(5):595-600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2003.08.034
11. Castel E, Lazennec JY, Chiras J, Enkaoua E, Saillant G. Acute spinal cord compression due to intraspinal bleeding from a vertebral hemangioma: two case-reports. Eur Spine J 1999;8(3):244-8.
https://doi.org/:10.1007/s005860050167
12. Ahn H, Jhaveri S, Yee A, Finkelstein J. Lumbar vertebral hemangioma causing cauda equina syndrome: a case
report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30(21):662-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000184560.78192.f6
13. Nguyen JP, Djinjian M, Pavlovitch JM, Badiane S. Vertebral hemangioma with neurologic signs: therapeutic results. Neurochirurgie 1989;35(5):299-303, 305-8. PMID: 2630927
14. Campanacci M. Hemangioma. En: Campanacci M (ed.). Bone and soft tissue tumors. Padova: Piccin Nuova Libraria &Wien: Springer; 1999:599-618.
15. Nurick S. The pathogenesis of the spinal cord disorder associated with cervical spondylosis. Brain 1972;95(1):87-100. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/95.1.87
16. Tetreault L, Kopjar B, Nouri A, Arnold P, Barbagallo G, Bartels R, et al. The modified Japanese Orthopaedic
Association scale: establishing criteria for mild, moderate and severe impairment in patients with degenerative
cervical myelopathy. Eur Spine J 2017;26(1):78-84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4660-8
17. Persaud T. The polka-dot sign. Radiology 2008;246(3):980-1. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2463050903
18. Wang B, Zhang L, Yang S, Han S, Jiang L, Wei F, et al. Atypical radiographic features of aggressive vertebral
hemangiomas. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2019;101(11):979-86. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.18.00746
19. Acosta FL, Sanai N, Cloyd J, Deviren V, Chou D, Ames CP. Treatment of Enneking stage 3 aggressive vertebral
hemangiomas with intralesional spondylectomy: report of 10 cases and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech 2011;24(4):268-75. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181efe0a4
20. Qiu B, Joo P, Ajabnoor R, Boyce B, Mesfin A. Surgical management of aggressive hemangiomas of the spine. J Clin Neurosci 2020;78:67-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2020.06.012
21. Heiss JD, Doppman JL, Olfield EH. Brief report: relief of spinal cord compression from vertebral hemangioma by intralesional injection of absolute etanol. N Engl J Med 1994;331(8):508-11. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199408253310804
22. Hekster REM, Luyendijk W, Tan TI. Spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangiomas relieved by
percutaneous catheter embolisation. Neuroradiology 1972;3:160-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341502
23. Hao J, Hu Z. Percutaneous cement vertebroplasty in the treatment of symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas. Pain Physician 2012;15(1):43-9. PMID: 22270737
24. Pinto M, Añon M, D’Innocenzo AC, Gomez AA, Zanabria Sosa C, Gonzalez FJ. Cifoplastia con balón para el
tratamiento de los hemangiomas vertebrales. Descripción de un caso y revisión bibliográfica. Rev Asoc Arg Ortop
Traumatol 2009;74(1):66-9. Disponible en: https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/2009/n1/art11.pdf
25. Garzon-Muvdi T, Iyer R, Goodwin CR, Abu-Bonsrah N, Orru E, Gailloud P, et al. Percutaneous embolization and
spondylectomy of an aggressive L2 hemangioma. Spine J 2016;16(3):167-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2015.10.001
26. Jaramillo Carling E. Compresión medular causada por hemangioma vertebral. Presentación de un caso y análisis de la literatura médica. Rev Colomb Ortop Traumatol 2005;19(1):86-9. Disponible en: http://www.sccot.org.co/pdf/RevistaDigital/19-01-2005/14Compresion.pdf
27. Sewell MD, Dbeis R, Bliss P, Watkinson T, Hutton M. Radiotherapy for acute, high-grade spinal cord compression caused by vertebral hemangioma. Spine J 2016;16(3):195-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2015.10.018
28. Rades D, Bajrovic A, Alberti W, Rudat V. Is there a dose-effect relationship for the treatment of symptomatic
vertebral hemangioma? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;55(1):178-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03734-3
29. Kaoudi A, Capel C, Chenin L, Peltier J, Lefranc M. Robot-assisted radiofrequency ablation of a sacral s1–s2
aggressive hemangioma. World Neurosurg 2018;116:226-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.060
30. Manning HJ. Symptomatic hemangioma of the spine. Radiology 1951;56(1):58-65. https://doi.org/10.1148/56.1.58
31. Raco A, Ciappetta P, Artico M, Salvati M, Guidetti G, Guglielmi G. Vertebral hemangiomas with cord compression: the role of embolization in five cases. Surg Neurol 1990;34(3):164-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(90)90067-y
32. Grau SJ, Holtmannspoetter M, Seelos K, Tonn JC, Siefert A. Giant multilevel thoracic hemangioma with spinal
cord compression in a patient with Klippel-Weber-Trenaunay syndrome: case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976)
2009;34(14):E498-E500. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a4e4b8
33. Wang GX, Mu YD, Che JY, Zhang GF, Jiang G, Gao CP. Compressive myelopathy and compression fracture of
aggressive vertebral hemangioma after parturition: A case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore)
2019;98(50):e18285. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018285