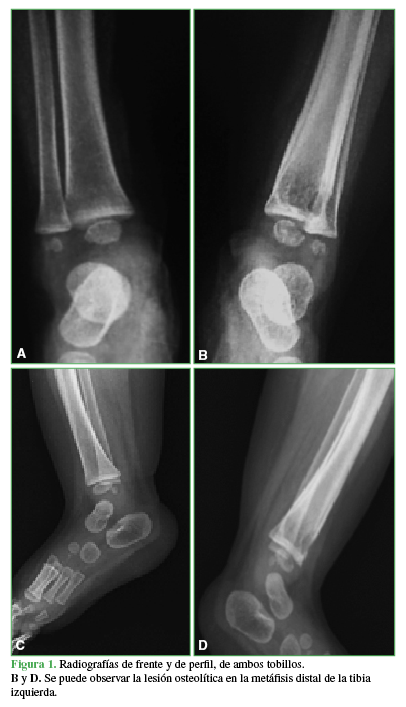
Tibia osteomyelitis secondary to BCG vaccination in an immunocompetent infant. Case report
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, used to prevent severe forms of tuberculosis (TB), is the most extensively used vaccine worldwide. Adverse events associated with BCG vaccination are rare, and most of them occur at the inoculation site. We present a tibia Osteomyelitis case secondary to BCG vaccination in an immunocompetent infant.
Conclusions: Bone involvement secondary to BCG vaccination in previously healthy patients is extremely rare. Healthcare providers must consider such settings in order to make the diagnosis and institute the appropriate treatment. Antituberculous drugs produced good therapeutic results with no need for surgical toilette.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
2. Ministerio de Salud de la República Argentina. Recomendaciones Nacionales de Vacunación Argentina 2012. http://www.msal.gob.ar/images/stories/bes/graficos/0000000451cnt-2013-06_recomendaciones-vacunacion-argentina-2012.pdf
3. Organización Mundial de la Salud. Hoja de información sobre las tasas observadas de reacciones a vacunas. Vacuna Bacilo de Calmette-Guérin (BCG); 2012. https://www.who.int/vaccine_safety/initiative/tools/BCG_Vaccine_rates_information_sheet_ES.pdf?ua=1
4. Ministerio de Salud de la República Argentina. Vacunación Segura: Vigilancia de eventos supuestamente atribuibles a la vacunación o inmunización (ESAVI); 2012. http://www.msal.gob.ar/images/stories/bes/graficos/0000000448cnt-2014-01_manual-vacunacion-segura-esavi.pdf
5. Lotte A, Wasz-Hockert O, Poisson N, Engbaek H, Landmann H, Quast U, et al. Second IUATLD study on complications induced by intradermal BCG-vaccination. Bull Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis 1988;63(2):47-59. PMID: 3066422
6. Organización Mundial de la Salud. Documento de posición de la OMS sobre las vacunas BCG. Boletín Epidemiológico Semanal 2018;8(93):73-96. http://www9.who.int/immunization/policy/position_papers/pp_bgc_2018_ES.pdf
7. Lin WL, Chiu NC, Lee PH, Huang AS, Huang FY, Chi H, et al. Review management of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin osteomyelitis/osteitis in immunocompetent children-A systematic review. Vaccine 2015;33(36):4391-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.07.039