Evaluación de la estabilización de fracturas expuestas de pierna grados I y II de Gustillo en la etapa aguda
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
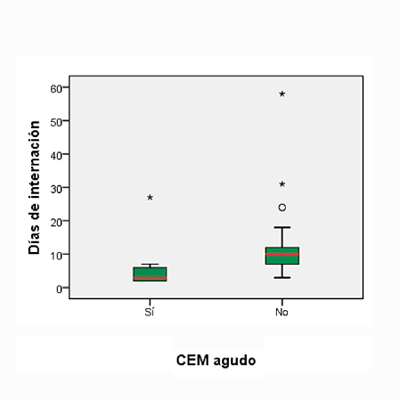
Pacientes y Métodos: Se realizó un estudio de cohorte retrospectivo sobre el tratamiento en la etapa aguda de los pacientes que ingresaron en el hospital con fracturas expuestas de pierna entre 2015 y 2018. Se analizó la tasa de infecciones durante los primeros 6 meses después de la cirugía y se comparó la fijación en la etapa aguda con la fijación diferida.
Resultados: La fijación interna con clavos endomedulares en la etapa aguda, en pacientes con fracturas expuestas de pierna no aumentó, sino que disminuyó la tasa de infecciones en el control posoperatorio.
Conclusión: El estudio avala la colocación de clavos endomedulares en la etapa aguda, en pacientes con fractura de tibia expuestas.
Nivel de Evidencia: II
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo
La aceptación del manuscrito por parte de la revista implica la no presentación simultánea a otras revistas u órganos editoriales. La RAAOT se encuentra bajo la licencia Creative Commons 4.0. Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Se puede compartir, copiar, distribuir, alterar, transformar, generar una obra derivada, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente la obra, siempre que: a) se cite la autoría y la fuente original de su publicación (revista, editorial y URL de la obra); b) no se usen para fines comerciales; c) se mantengan los mismos términos de la licencia.
En caso de que el manuscrito sea aprobado para su próxima publicación, los autores conservan los derechos de autor y cederán a la revista los derechos de la publicación, edición, reproducción, distribución, exhibición y comunicación a nivel nacional e internacional en las diferentes bases de datos, repositorios y portales.
Se deja constancia que el referido artículo es inédito y que no está en espera de impresión en alguna otra publicación nacional o extranjera.
Por la presente, acepta/n las modificaciones que sean necesarias, sugeridas en la revisión por los pares (referato), para adaptar el trabajo al estilo y modalidad de publicación de la Revista.
Citas
worth? J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7(6):1125-30. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2013/5504.3081
2. Chapman MW, Oslon SA. Open fractures. En: Rockwood’s and Green’s fracture in adults, 4th ed. Philadelphia:
Lippincott-Raven; 1996:305-52.
3. Kakar S, Tornetta P 3rd. Open fractures of the tibia treated by immediate intramedullary tibial nail insertion without reaming: a prospective study. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21(3):153-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3180336923
4. Uchiyama Y, Kobayashi Y, Ebihara G, Hamahashi K, Watanabe M. Retrospective comparison of postoperative
infection and bone union between late and immediate intramedullary nailing of Gustilo grades I, II, and IIIA open tibial shaft fractures. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open 2016;1:1-4. https://doi.org/10.1136/tsaco-2016-000035
5. Nicoll EA. Fractures of the tibial shaft: A survey of 705 cases. J Bone J Surg Br 1964;46:337. PMID: 14216447
6. Craig J, Fuchs T, Jenks M, Fleetwood K, Franz D, Iff J, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the additional
benefit of local prophylactic antibiotic therapy for infection rates in open tibia fractures treated with intramedullary nailing. Int Orthop (SICOT) 2014;38:1025-30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2293-2J
7. Metsemakers WJ, Handojo K, Reynders P, Sermon A, Vanderschota P, Nijs S. Individual risk factors for deep
infection and compromised fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures: A single centre
experience of 480 patients. Injury 2015;46(4):740-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.12.018
8. Ziran BH, Darowish M, Klatt BA, Agudelo JF, Smith WR. Intramedullary nailing in open tibia fractures: a
comparison of two techniques. Int Orthop 2004;28(4):235-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-004-0567-9
9. Yokoyama K, Itoman M, Uchino M, Fukushima K, Nitta H, Kojima Y. Immediate versus delayed intramedullary
nailing for open fractures of the tibial shaft: a multivariate analysis of factors affecting deep infection and fracture healing. Indian J Orthop 2008;42(4):410-9. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.43385
10. Gopal S, Giannoudis PV, Murray A, Matthews SJ, Smith RM. The functional outcome of severe, open tibial
fractures managed with early fixation and flap coverage. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86(6):861-7.
https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.86b6.13400
11. Haonga BT, Liu M, Albright P, Challa ST, Ali SH, Lazar AA, et al. Intramedullary nailing versus external fixation
in the treatment of open tibial fractures in Tanzania: results of a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am
2020;102(10):896-905. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.19.00563
12. Okike K, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in the management of open fractures. A critical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2006;88(12): 2739-48. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.F.00146
13. Olson SA, Schemitsch EH. Open fractures of the tibial shaft. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1996;78:1428-37. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scieloOrg/php/reflinks.php?refpid=S0138-6557200200020000700002&lng=es&pid=S0138-65572002000200007
14. Worlock P, Slack R, Harvey L, Mawhinney R. The prevention of infection in open fractures: an experimental study of the effect of fracture stability. Injury 1994;25(1):31-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1383(94)90181-3
15. Bach AW, Hansen ST Jr. Plates versus external fixation in severe open tibial shaft fractures. A randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1989;(241):89-94. PMID: 2924483
16. Shah RK, Moehring HD, Singh RP, Dhakal A. Surgical Implant Generation Network (SIGN) intramedullary nailing of open fractures of the tibia. Int Orthop 2004;28(3):163-6. https://doi-org/10.1007/s00264-003-0535-9
17. Bhandari M, Guyatt GH, Swiontkowski MF, Schemitscch EH. Treatment of open fracture shaft of tibia: a systematic overview and metaanalysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2000;83:62-8. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.83B1.0830062
18. Oh CW, Park BC, Ihn JC, Park HJ. Primary unreamed intramedullary nailing for open fractures of the tibia. Int
Orthop (SICOT) 2001;24:338-41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002640000174
19. Chapman MW. The use of immediate internal fixation in open fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 1980;11:579-91. PMID: 6106173
20. Tielinen L, Lindahl JE, Tukiainen EJ. Acute unreamed intramedullary nailing and soft tissue reconstruction with
muscle flaps for the treatment of severe open tibial shaft fractures. Injury 2007;38(8):906-12.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2007.02.052
21. Moghtadaei M, Otoukesh B, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Boddouhi B, Yeganeh A. Evaluation of inflammatory response in patients undergoing surgical treatment for early and delayed femoral fractures. Arch Med Sci 2019;15(1):141-5. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2016.63013
22. Gasser B, Tiefenboeck TM, Boesmueller S, Kivaranovic D, Bukaty A, Platzer P. Damage control surgery -
experiences from a level I trauma center. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2017;18(1):391. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1751-6
23. Schächter S. ¿Qué nos enseñaron 40 años de experiencia en el tratamiento de las fracturas de la pierna? Rev Asoc Argent Ortop Traumatol 1996;61(3):368-74. Disponible en: https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/1993_2002/1996/1996_3/610312.pdf
24. Río M, Colombo M, Gabas D, Angheben E, Gotter G, Saa YA. Fracturas expuestas graves en los miembros
inferiores: nuestro protocolo de tratamiento. Rev Asoc Argent Ortop Traumatol 2006;71(1):32-7. Disponible en:
https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/2006/n1_vol71/art5.pdf
25. Anglen JO, Blue JM. A comparison of reamed and unreamed nailing of the tibia. J Trauma 1995;39(2):351-5.
https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-199508000-00027
26. Finkemeier CG, Schmidt AH, Kyle RF, Templeman DC, Varecka TF. A prospective, randomized study of
intramedullary nails inserted with and without reaming for the treatment of open and closed fractures of the tibial shaft. J Orthop Trauma 2000;14:187-93. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-200003000-00007
27. Schemitsch EH, Bhandari M, Guyatt G, Sanders DW, Swiontkowski M, Tornetta P, et al. Prognostic factors for
predicting outcomes after intramedullary nailing of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2012;94:1786-93.
https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01418
28. Río M. Actualización en fracturas expuestas. Evidencia actual. Rev Asoc Argent Ortop Traumatol 2008;74(4):415-20. Disponible en: https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/2008/n4_vol73/art14.pdf